S-75 Dvina
| S-75 Dvina (NATO reporting name: SA-2 Guideline) |
|
|---|---|
 S-75 including V-750 missile on camouflaged launcher |
|
| Type | Strategic SAM system |
| Place of origin | |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1957-present |
| Used by | See list of present and former operator |
| Wars | Vietnam War, Six-Day War, Cold War, Iran-Iraq War, Gulf War, War in Abkhazia (1992–1993) |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Lavochkin OKB |
| Designed | 1953-1957 |
| Produced | 1957 |
| Number built | about 4600 missiles produced |
| Variants | S-75 Dvina, S-75M-2 Volkhov-M, S-75 Desna, S-75M Volkhov, S-75M Volga |
The Lavochkin OKB S-75 (Russian: С-75; NATO reporting name SA-2 Guideline) is a Soviet designed high-altitude, command guided, surface-to-air missile (SAM) system. Since its first deployment in 1957, it has become the most widely deployed and used air defense missile in history.
This system first gained fame when an S-75 battery shot down a CIA U-2 overflying the Soviet Union in 1960. Later, North Vietnamese forces used the S-75 extensively during the Vietnam War to defend Hanoi and Haiphong. It has also been locally-produced in the People's Republic of China using the names HQ-1 and HQ-2. Other nations have produced so many local variants combining portions of the S-75 system with both indigenously developed components or third party systems, that it has become virtually impossible to find a pure S-75 system today.
Contents |
History
Development
In the early 1950s, the United States Air Force rapidly accelerated its development of long range jet bombers carrying nuclear weapons. The USAF program led to the deployment of Boeing B-47 Stratojet supported by aerial refueling aircraft to extend its range deep into the Soviet Union. The USAF quickly followed the B-47 with the development of the Boeing B-52 Stratofortress with greater range and payload than the B-47. The range, speed and payload of these U.S. bombers posed a significant threat to the Soviet Union in the event of a war between the two countries.
Consequently, the Soviets initiated the development of improved air defense systems. Although the Soviet Air Defense Forces had large numbers of anti-aircraft artillery (AAA), including radar-directed batteries, the limitations of guns versus high altitude jet bombers was obvious. Therefore, the Soviet Air Defense Forces began the development of missile systems to replace the World War II vintage gun defenses.
In 1953, Lavochkin OKB began the development of what became the S-75 under the direction of Pyotr Grushin. This program focused on producing a missile which could bring down a large, non-maneuvering, high-altitude aircraft. As such it did not need to be highly maneuverable, merely fast and able to resist aircraft counter-measures. For such a pioneering system, development proceeded rapidly and testing began a few years later. In 1957, the wider public first became aware of the S-75 when the missile was shown at that year's May Day parade in Moscow.
Initial deployment
Wide scale deployment started in 1957, with various upgrades following over the next few years. The S-75 was never meant to replace the S-25 Berkut surface to air missile sites around Moscow, but it did replace high-altitude anti-aircraft guns, such as the 130 mm KS-30 and 100 mm KS-19. Between mid-1958 and 1964 U.S. intelligence assets located more than 600 S-75 sites in the USSR. These sites tended to cluster around population centers, industrial complexes, and government control centers. A ring of sites was also located around likely bomber routes into the Soviet heartland. By the mid-1960s, the Soviet Union had ended the deployment of the S-75 with perhaps 1,000 operational sites.
In addition to the Soviet Union, several S-75 batteries were deployed during the 1960s in East Germany to protect Soviet forces stationed in that country. Later the system was sold to most Warsaw Pact countries and was provided to China, North Korea and eventually, North Vietnam.
Employment
While the shooting down of Francis Gary Powers U-2 in 1960 is the first publicized success for the S-75, the first aircraft actually shot down by the S-75 was a Taiwanese RB-57 high-altitude reconnaissance aircraft. In this case, the aircraft was hit by a Chinese operated S-75 site near Beijing on October 7, 1959. Over the next few years the Taiwanese ROCAF would lose a number of aircraft to the S-75, both RB-57's and various drones. On May 1, 1960, Gary Powers' U-2 was shot down while flying over the testing site near Sverdlovsk, although it is thought to have taken 14 missiles to hit his high-flying plane. That action led to the U-2 Crisis of 1960. It is also believed that Chinese S-75 downed some ROCAF-piloted U-2s based on Taiwan.
During the Cuban Missile Crisis, a U-2 piloted by USAF Major Rudolf Anderson was shot down over Cuba by an S-75 in October 1962.[1]
In 1965 North Vietnam asked for some assistance against the U.S.'s airpower, to which they were essentially defenseless at the time. After some discussion it was agreed to supply the PAVN with the S-75, although the decision was not taken lightly as it greatly increased the chances that one would fall into US hands for study. Site preparation started early in the year, and the US detected the program almost immediately on April 5, 1965. While military planners pressed for the sites to be attacked before they could become operational, their political leaders refused, fearing that Soviet technical staff might be killed.
Then on July 23 1965, a US Navy F-4B aircraft was shot down. The US responded with Operation Iron Hand three days later to attack the other sites before they could become operational. Most of the S-75 were deployed around the Hanoi-Haiphong area and were off limits to attack (as were local airfields) for political reasons. President Lyndon Johnson announced on public TV that one of the other sites would be attacked the next week. The Vietnamese removed the missiles and replaced them with decoys, while moving every available anti-aircraft gun into the approach routes. The tactic worked, causing American casualties.
The system was used widely throughout the world, especially in the Middle East, where Egypt and Syria used them to defend against Israeli Air Force, where the air defense net accounted for the majority of the downed Israeli aircraft. A success of the missile occurred during Desert Storm when an F-14 was shot down by a SAM believed to have been an S-75 on 21 January 1991. The last apparent success seems to have occurred during the War in Abkhazia (1992–1993) when Georgian missiles shot down a Russian Su-27 fighter near Gudauta on March 19, 1993.[1]
The standard S-75 SAM is also capable of being used against land targets, and its crews were taught how to aim the missile. Recent pictures have shown Iranian S-75s fired in surface-surface mode.
Countermeasures and counter-countermeasures
Over the next year the US delivered a number of solutions to the S-75 problem. The Navy soon had the Shrike missile in service, and mounted their first offensive strike on a site in October. The Air Force responded by fitting B-66 bombers with powerful jammers that blinded the early warning radars, and developed smaller jamming pods for fighters which denied range information to the radars. Later developments included the Wild Weasel aircraft fitted with jammer pods and ECM systems, dedicated to jamming and then shooting the sites with Shrikes of their own.
The Soviets and Vietnamese, however, were able to adapt to some of these tactics. The USSR upgraded the radar several times to improve ECM resistance. They also introduced a passive guidance mode, whereby the missile could lock on the jammer itself. This had an added advantage, since the radar could be kept off thus preventing Shrikes from being fired. Moreover, some new tactics were developed to combat the Shrike. One of them was to point the radar to the side and then turn it off briefly. Since the Shrike was a relatively primitive anti-radiation missile, it would follow the beam away from the radar and then simply crash when it lost the signal (after the radar was turned off). Another was a "false launch", when the tracking radar was turned on but the missiles were not actually fired. This allowed the missile crew to see if the target was equipped with a Shrike. If the aircraft fired one, it could be neutralized with the above technique without sacrificing any missiles.
Despite these advances, the US was able to come up with effective ECM packages for the B-52E models. These planes were able to fly raids against Hanoi with relatively few losses (though still significant enough to cause some concern, see Linebacker 2).
Replacement systems
Soviet Air Defence Forces started to replace the S-75 with the vastly superior SA-10 and SA-12 systems in the 1980s. Today only a few hundred, if any, of the 4,600 missiles are still in Russian service, even though they underwent a modernization program as late as 1993.
The S-75 remains in widespread service throughout the world, with some level of operational ability in 35 countries. Vietnam and Egypt are tied for the largest deployments at 280 missiles each, while North Korea has 270, and Poland has 240. The Chinese also deploy the HQ-2, an upgrade of the S-75, in relatively large numbers.
Description
Soviet doctrinal organization
The Soviet Union used a fairly standard organizational structure for S-75 units. Other countries that have employed the S-75 may have modified this structure. Typically, the S-75 is organized into a regimental structure with three subordinate battalions. The regimental headquarters will control the early-warning radars and coordinate battalion actions. The battalions will contain several batteries with their associated acquisition and targeting radars.
Site layout
Each battalion will typically have six semi-fixed, single-rail launchers for their V-750 missiles positioned approximately 60-100 meters apart from each other in a hexagonal "flower" pattern with radars and guidance systems placed in the center. It was this unique "flower" shape that led to the sites being easily recognizable in reconnaissance photos. Typically another six missiles are stored on tractor-trailers near the center of the site.
Missile
| V-750 | |
|---|---|
 V-750V 1D missile on a launcher |
|
| Type | Surface-to-air missile |
| Place of origin | |
| Production history | |
| Variants | V-750, V-750V, V-750VK, V-750VN, V-750M, V-750SM, V-750AK |
| Specifications (V-750[2]) | |
| Weight | 2300 kg |
| Length | 10,600 mm |
| Diameter | 700 mm |
|
|
|
| Warhead | Frag-HE |
| Warhead weight | 200 kg |
| Detonation mechanism |
Command |
|
|
|
| Propellant | Solid-fuel booster and a storable liquid-fuel upper stage |
| Operational range |
45 kilometres (28 mi) |
| Flight altitude | 20,000 metres (66,000 ft) |
| Boost time | 5 s boost, then 20 s sustain |
| Speed | Mach 3.5 |
| Guidance system |
radio control guidance |
| Accuracy | 65 m |
| Launch platform |
Single rail, ground mounted (not mobile) |
The V-750 is a two-stage missile, consisting of a solid-fuel booster and a storable liquid-fuel upper stage burning red fuming nitric acid as the oxidizer, and kerosene as the fuel. The booster fires for about 4–5 seconds, and the main engine for about 22 seconds, by which time the missile is traveling at about Mach 3. The booster mounts four large cropped-delta wing fins with small control surfaces in their trailing edges, used to control roll. The upper stage has smaller cropped-deltas near the middle of the airframe, with a smaller set of control surfaces at the extreme rear and (in most models) much smaller fins on the nose.
The missiles are guided using radio control signals from the guidance computers at the site, sent on one of three channels. The earlier S-75 models received their commands via two sets of four small antennas in front of the forward fins, while the D models and on used four much larger strip antennas running between the forward and middle fins. The guidance system at an S-75 site can handle only one target at a time, but can direct three missiles against it. Additional missiles could be fired against the same target after one or more missiles of the first salvo had completed their run and the radio channel was freed.
The missile typically mounts a 195 kg (430 lb) fragmentation warhead, with proximity, contact and command fusing. The warhead has a lethal radius of about 65 m (215 ft) at lower altitudes, while at higher altitudes the thinner atmosphere allows for a wider radius of up to 250 m (820 ft). The missile itself is accurate to about 75 m (250 ft), which explains why two were typically fired in a salvo. One version, the SA-2E, mounted a 295 kg (650 lb) nuclear warhead of an estimated 15 kt yield, or a conventional warhead of similar weight.
Typical range for the missile is about 45 km (30 miles), with a maximum altitude around 20,000 m (60,000 ft). The radar and guidance system imposed a fairly long short-range cutoff of about 500-1,000 m (3,000 ft), making them fairly safe to attack at low level.
Missiles from SA-2 Guideline (all versions SA-75 / S-75)
| Missile | Factory index | Character |
|---|---|---|
| V-750 | 1D | Firing range 7 – 29 km, Firing altitude 3000 – 23000 m |
| V-750V | 11D | Firing range 7 – 29 km, Firing altitude 3000 – 25000 m, Weight 2163 kg, Length 10726 mm, Warhead weight 190 kg, Diameter 500 / 654 mm |
| V-750VK | 11D | Modernized missile |
| V-750VM | 11DM | Missile for firing to aircraft - jammer |
| V-750VM | 11DU | Modernized missile |
| V-750VM | 11DА | Modernized missile |
| V-750M | 20ТD | No specific information available |
| V-750SM | - | No specific information available |
| V-750VN | 13D | Firing range 7 - 29/34 km, Firing altitude 3000 - 25000/27000 m, Length 10841 mm |
| - | 13DА | Missile with new warhed weight 191 kg |
| V-750АK | - | No specific information available |
| V-753 | 13DM | Missile from naval SAM system M-2 Volkhov-M (SA-N-2 Guideline) |
| V-755 | 20D | Firing range 7 – 43 km, Firing altitude 3000 – 30000 m, Weight 2360 – 2396 kg, Length 10778 mm, Warhead weight 196 kg |
| V-755 | 20DP | Missile for firing on passive flight-line, Firing range 7 – 45 km active, 56 km passive , Firing altitude 300 - 30000 (35000) m |
| V-755 | 20DА | Missile with expired guarantee period and remodelled to 20DS |
| V-755OV | 20DO | Missile for taking air samples |
| V-755U | 20DS | Missile with selectvive block for firing to target in low altitude (under 200 m), Firing altitude 100 - 30000 / 35000 m |
| V-755U | 20DSU | Missile with selectvive block for firing to target in low altitude (under 200 m) and shortening time preparation missile to fire, Firing altitude 100 - 30000 / 35000 m |
| V-755U | 20DU | Missile with shortening time preparation missile to fire |
| V-759 | 5Ja23 (5V23) | Firing range 6 - 56 (or 60 or 66) km, Firing altitude 100 - 30000 / 35000 m, Weight 2406 kg, Length 10806 mm, Warhead weight 197 – 201 kg |
| V-760 | 15D | Missile with nuclear warhead |
| V-760V | 5V29 | Missile with nuclear warhead |
| V-750IR | - | Missile with pulse radiofuse |
| V-750N | - | Test missile |
| V-750P | - | Experimental missile - with rotate wings |
| V-751 | KM | Experimental missile - flying laboratory |
| V-752 | - | Experimental missile - boosters at the sides |
| V-754 | - | Experimental missile - with semi-active homing head |
| V-757 | 17D | Experimental Missile - with scramjet |
| - | 18D | Experimental Missile - with scramjet |
| V-757Kr | 3M10 | Experimental Missile - version for2K11 Krug (SA-4 Ganef) |
| V-758 (5 JaGG) | 22D | Experimental Missile - three-stage missile, Weirht 3200 kg, Speed 4,8 M (= 1560 m/s = 5760 km/h) |
| Korshun | - | Target missile |
| RM-75MV | - | Target missile - for low altitude |
| RM-75V | - | Target missile - for high altitude |
| Sinitsa-23 | 5Ja23 | Target missile |
Radar

The S-75 typically uses the Spoon Rest early warning radar which has a range of about 275 km (170 miles). The Spoon Rest provides early detection of incoming aircraft which are then handed off to the acquisition Fan Song radar. These radars, having a range of about 65 km (40 miles), are used to refine the location, altitude, and speed of the hostile aircraft. The Fan Song system consists of two antennas operating on different frequencies, one providing elevation (altitude) information and the other azimuth (bearing) information. Regimental headquarters also include a Spoon Rest, as well as a Flat Face long-range C-band radar and Side Net height-finder. Information from these radars is sent from the regiment down to the battalion Spoon Rest operators to allow them to coordinate their searches. Earlier S-75 versions used a targeting radar known as Knife Rest, which was replaced in Soviet use, but can still be found in older installations.
Major variants
Upgrades to anti-aircraft missile systems typically combine improved missiles, radars and operator consoles. Usually missile upgrades drive changes to other components to take advantage of the missile's improved performance. Therefore, when the Soviets introduced a new S-75, it was paired with an improved radar to match the missile's greater range and altitude.
- SA-2A; S-75 Dvina (Двина - Dvina River) with Fan Song-A guidance radar and V-750 or V-750V missiles. Initial deployment began in 1957. The combined missile and booster was 10.6 m (34.8 ft) long, with a booster having a diameter of 0.65 m (25.5 in), and the missile a diameter of 0.5 m (19.7 in). Launch weight is 2287 kg (5,041 lb). The missile has a maximum effective range of 30 km (19 miles), a minimum range of 8 km (5 miles) and an intercept altitude envelope of between 450 and 25,000 m (1,500-82,000 ft).
- SA-N-2A; S-75M-2 Volkhov-M (Russian Волхов - Volkhov River): Naval version of the A model fitted to the Sverdlov Class cruiser Dzerzhinski. Generally considered unsuccessful and not fitted to any other ships.
- SA-2B; S-75 Desna (Russian Десна - Desna River). This version featured upgraded Fan Song-B radars with V-750VK and V-750VN missiles. The second deployment version, the B model entered service in 1959. The missiles were slightly longer than the A versions, at 10.8 m (35.4 ft), due to a more powerful booster. The SA-2B could engage targets at altitudes between 500 m and 30 km (1,640-98,450 ft) and ranges up to 34 km (21 miles).

- SA-2C; S-75M Volkhov. Once again, the new model featured an upgraded radar, the Fan Song-C, mated to an improved V-750M missile. Improved -2B deployed in 1961. The V-750M was externally identical to the V-750VK/V-750VN, but with improved performance for range up to 43 km (27 miles) and reduced lower altitude limits of 400 m (1,312 ft).
- SA-2D; Fan Song-E radar and V-750SM missiles. The V-750SM differed significantly from the A/B/C versions in having new antennas and a longer barometric nose probe. Several other differences were associated with the sustainer motor casing. The missile is 10.8 m (35.4 ft) long, has the same body diameters and warhead as the SA-2C, but the weight is increased to 2450 kg (5,400 lb). The effective maximum range is 43 km (27 miles), the minimum range is 6 km (4 miles) and the intercept altitude envelope is between 250 and 25000 m (820-82,000 ft). Improved aircraft counter measures led to the development of the Fan Song-E with its better antennas which could cut through heavy jamming.
- SA-2E: Fan Song-E radar and V-750AK missiles. Similar rocket to the D model, but with a bulbous warhead section lacking the older missile's forward fins. The SA-2E is 11.2 m (36.7 ft) long, has a body diameter of 0.5 m (19.7 in) and weighs 2450 kg (5,400 lb) at launch. The missile can be fitted with either a command detonated 15 kt nuclear warhead or a 295 kg (650 lb) conventional HE warhead.
- SA-2F: Fan Song-F radar and V-750SM missiles. After watching jamming in Vietnam and the Six-Day War render the SA-2 completely ineffective, the existing systems were quickly upgraded with a new radar system designed to help ignore wide-band scintillation jamming. The command system also included a home-on-jam mode to attack aircraft carrying strobe jammers, as well as a completely optical system (of limited use) when these failed. F's were developed starting in 1968 and deployed in the USSR later that year, while shipments to Vietnam started in late 1970.
- SA-2 FC: Latest Chinese version. Can track six targets simultaneously and is able to control 3 missiles simultaneously.
- S-75M Volga (Russian С-75М Волга - Volga River). Version from 1995.
As previously mentioned, most nations with S-75s have matched parts from different versions, from third party missile systems or have added locally produced components. This has created a wide variety of S-75 systems which meet local needs.
- HQ-1 (Hong Qi, Red Flag): Chinese version of SA-2 with additional ECCM electronics to counter the System-12 ECM aboard U-2s flown by the Republic of China Air Force Black Cat Squadron.
- HQ-2: Upgraded HQ-1 with additional ECCM capability to counter the System-13 ECM aboard U-2s flown by Republic of China Air Force Black Cat Squadron. Upgraded HQ-2s remain in service today, and the latest version utilizes passive phased array radar designated SJ-202, which is able to simultaneously track and engage multiple targets at 115 km and 80 km, respectively. The adoption of multifunction SJ-202 radar has eliminated the need to have multiple radars each with single function, and thus greatly improved the overall effectiveness of the HQ-2 air defense system. A target drone version is designated BA-6.
Operators
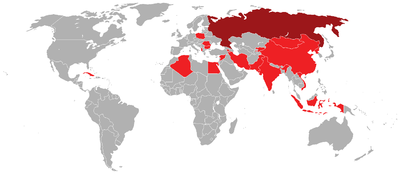
 Armenia - 250
Armenia - 250 Bulgaria - 18
Bulgaria - 18 People's Republic of China
People's Republic of China Cuba
Cuba Egypt - 240, Tayer el-Sabah variant
Egypt - 240, Tayer el-Sabah variant Iran - Up to 45 Launchers, HQ-2J and indigenous-produced Sayyad-1.
Iran - Up to 45 Launchers, HQ-2J and indigenous-produced Sayyad-1. Kyrgyzstan - few
Kyrgyzstan - few Mongolia
Mongolia Myanmar - 48 next 250 in 2008
Myanmar - 48 next 250 in 2008 North Korea - up to 270
North Korea - up to 270 Pakistan
Pakistan Romania
Romania Somaliland
Somaliland Syria - 275
Syria - 275 Tajikistan - few
Tajikistan - few Vietnam
Vietnam Yemen
Yemen Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe
Former operators
 Afghanistan
Afghanistan Algeria
Algeria Czechoslovakia - 23
Czechoslovakia - 23 East Germany
East Germany Georgia[1]
Georgia[1] Hungary
Hungary Indonesia
Indonesia India
India Iraq
Iraq Poland
Poland Russia
Russia Soviet Union - passed on to successor states
Soviet Union - passed on to successor states Yugoslavia - passed on to successor states
Yugoslavia - passed on to successor states Somalia - passed on to Somaliland
Somalia - passed on to Somaliland
Related content
| Wikisource has several original texts related to: Audio recordings and transcripts with comments of actual Wild Weasel combat missions over Vietnam. |
- 17D, rocket for S-75
- Project Nike Similar US medium-high altitude anti-air missile system
- Wild Weasel
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 http://mdb.cast.ru/mdb/3-2008/item3/article3/
- ↑ "V-750". http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/world/russia/v-75-specs.htm. Retrieved 2008-07-15..
External links
- Pakistan military info
- Russian site on the S-75 from Said Aminov "Vestnik PVO" (Russian)
- Russian site on the S-75 from Vitaly Kuzmin "Military Paritet" (Russian)
- S-75M3 Volkhov (SA-2e Guideline) Simulator
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||